What is Sniffing?
Sniffing refers to the process of intercepting and capturing network traffic, often used by attackers to eavesdrop on sensitive data such as usernames, passwords, and confidential communications Sniffers can be either hardware or software installed on the system, and by setting one up on a network in promiscuous mode, a malicious intruder can capture and analyze all of the network traffic.
Types of Sniffing Attacks:
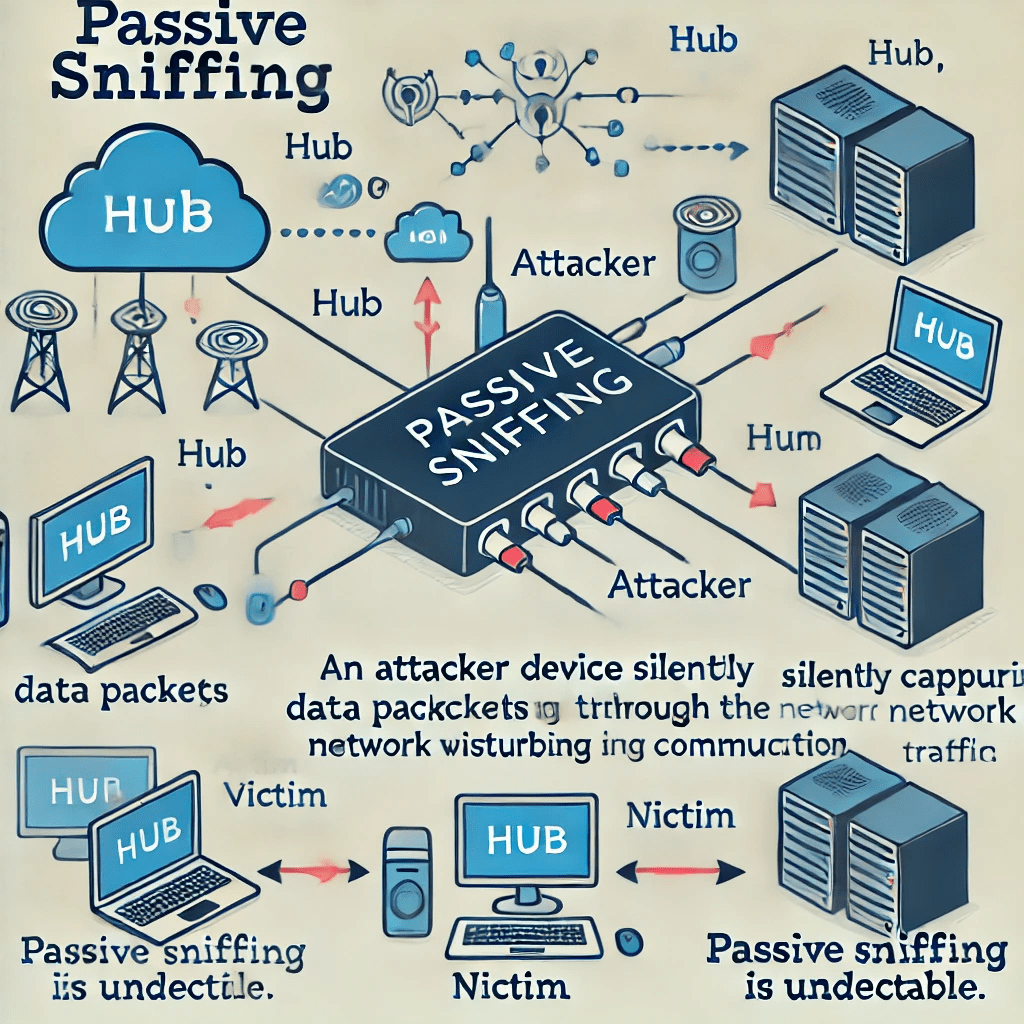
1. Passive Sniffing:
how passive sniffing operates without changing the network traffic, the attacker just listens to it. Usually, a hub or network segment is used for this, broadcasting all communication to every device.
Example Attacks:
- Eavesdropping on unencrypted/insecure traffic (e.g., HTTP, FTP).
- Capturing data transmitted in plain text.
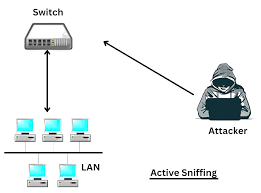
2. Active Sniffing:
Actively manipulating the network to capture traffic, commonly used in switch-based networks and Routers.it Often involves injecting malicious packets to redirect or duplicate the network traffic.
Techniques Used:
- ARP Spoofing (Poisoning): Create fake ARP responses to redirect traffic.
- MAC Flooding: MAC flooding floods a switch with fake MAC addresses.
- DNS Spoofing: Manipulating DNS responses to redirect traffic.