Background concept of CORS.
Cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) is a mechanism that allows using resources from any other domain. So, CORS introduced to eliminate some restrictions imposed by the SOP which block requests from accessing data on a Web Application unless it comes from the same origin. In simple words, Imaging the bing.com wants to access some data from another website, supposed youtube.com. This type of request wouldn’t be allowed under the browser’s SOP. However, by CORS request, youtube.com add a few special response headers that allow bing.com to use its data.
How to find CORS in your Target web application
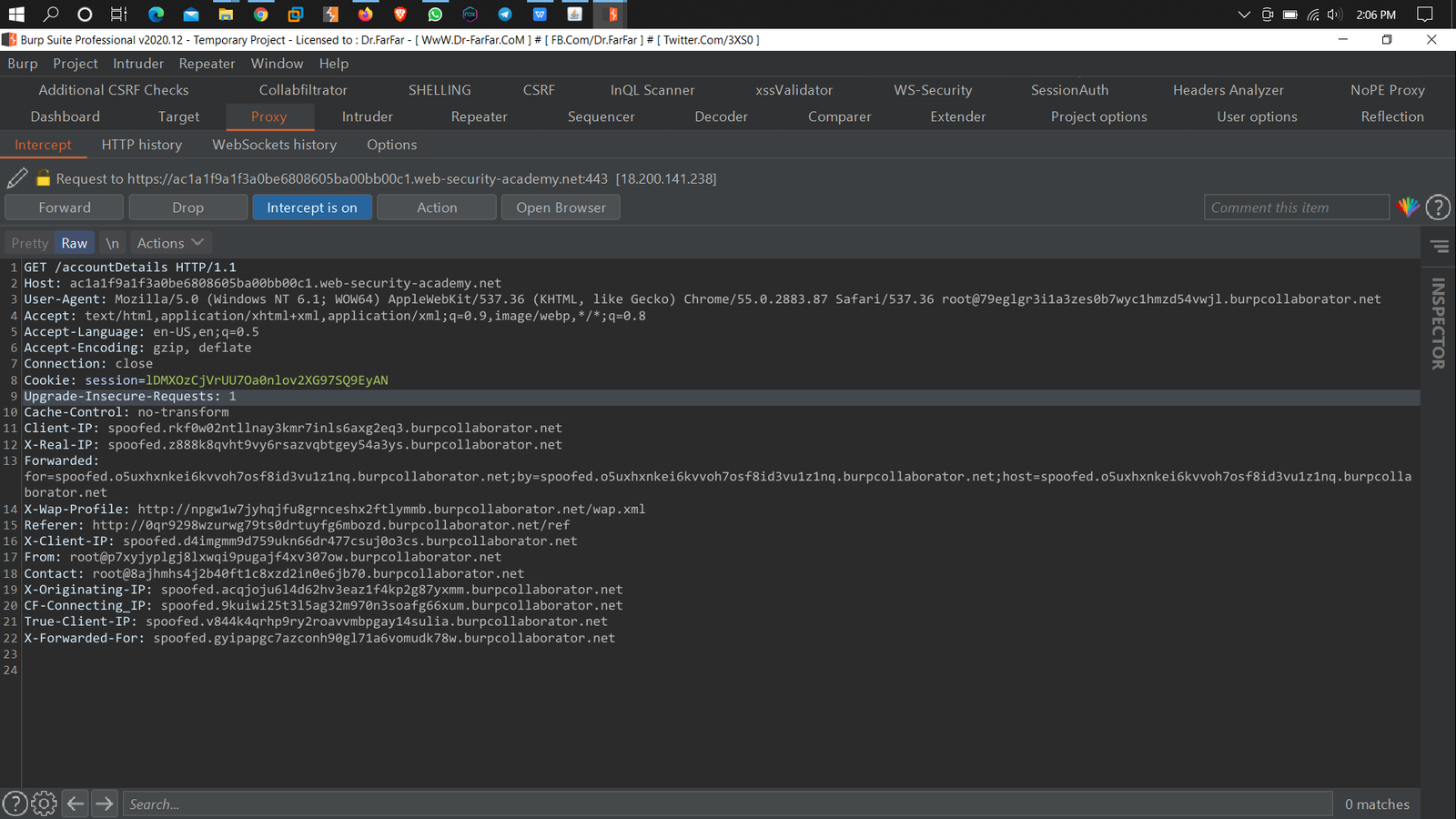
1. Capture the request in Burp suit
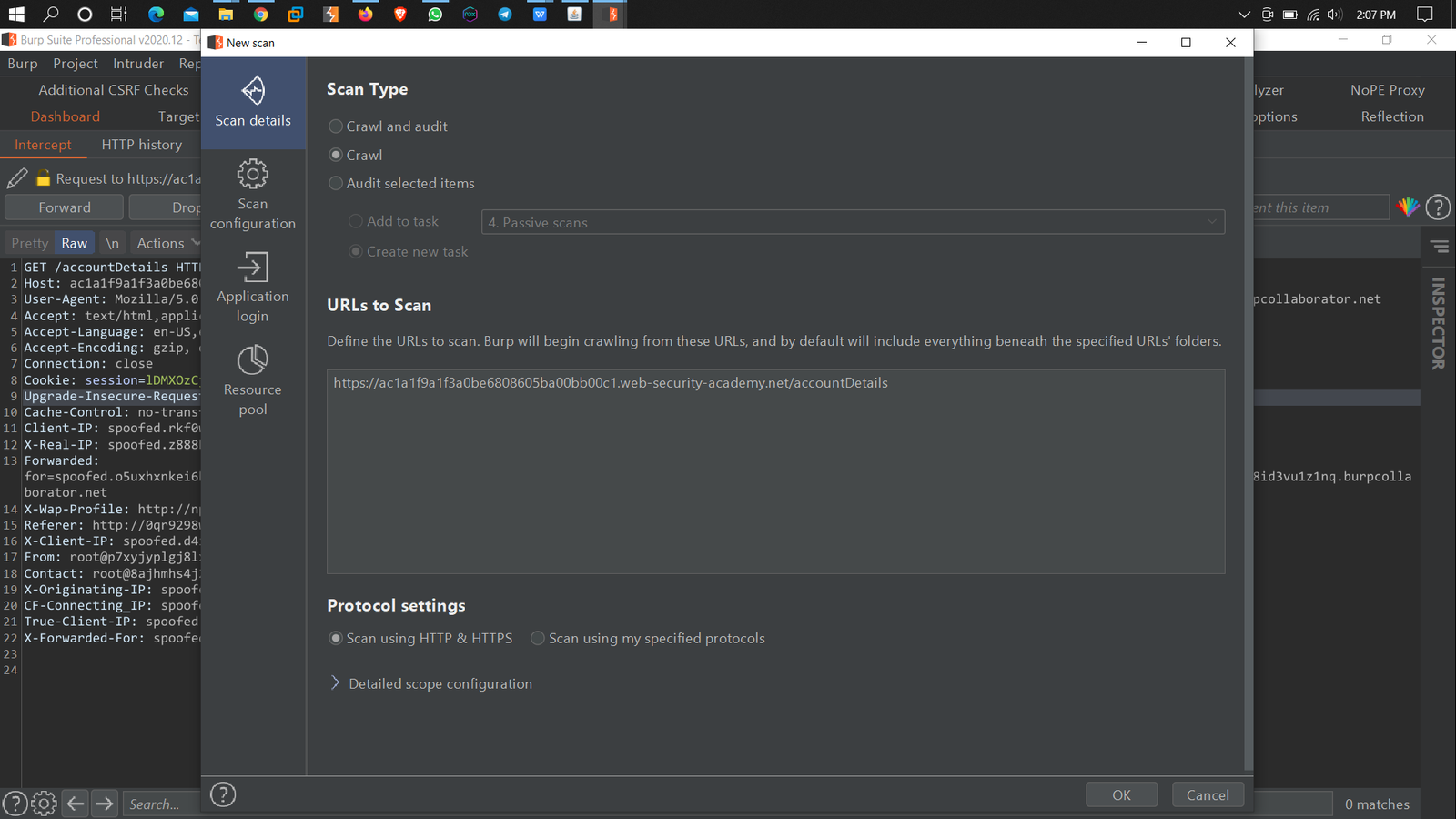
2. Crawl your target web application
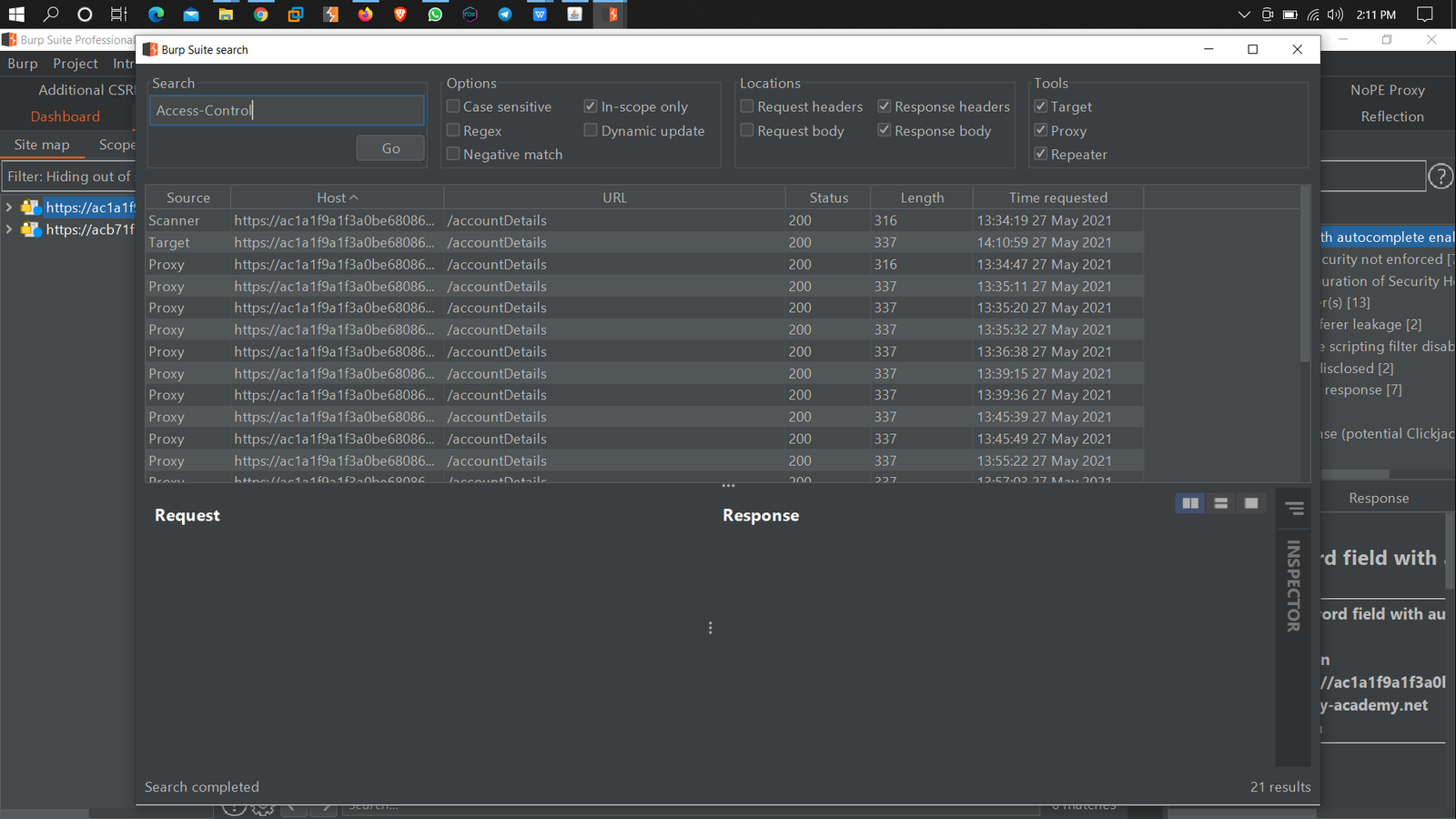
3. Now Search the “Access-Control-Allow-Origin" in the Response Header Using the Burp search
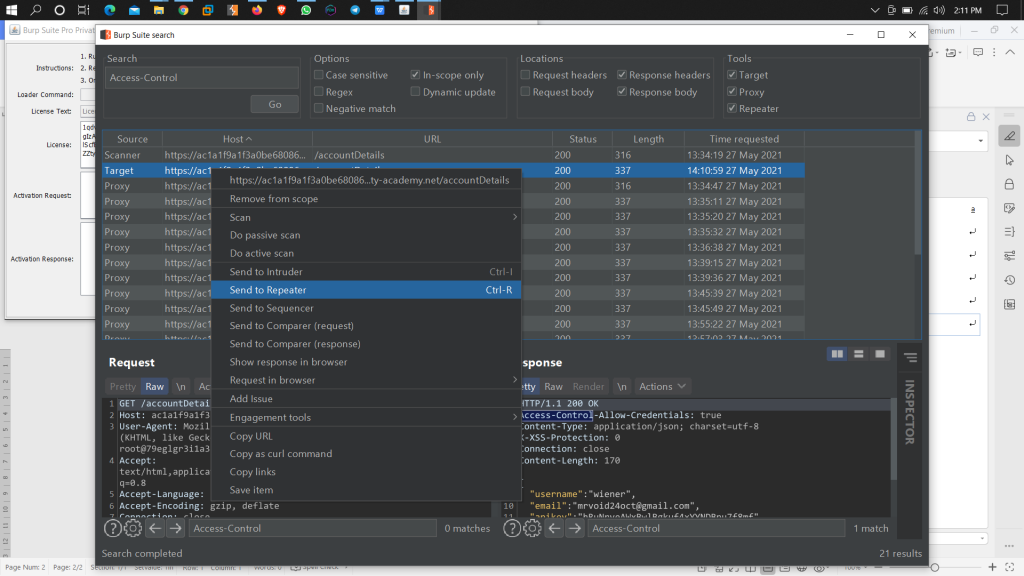
4. Now send that request in the Repeater
5. Add a Header in the request Body
Origin: Http://bing.com
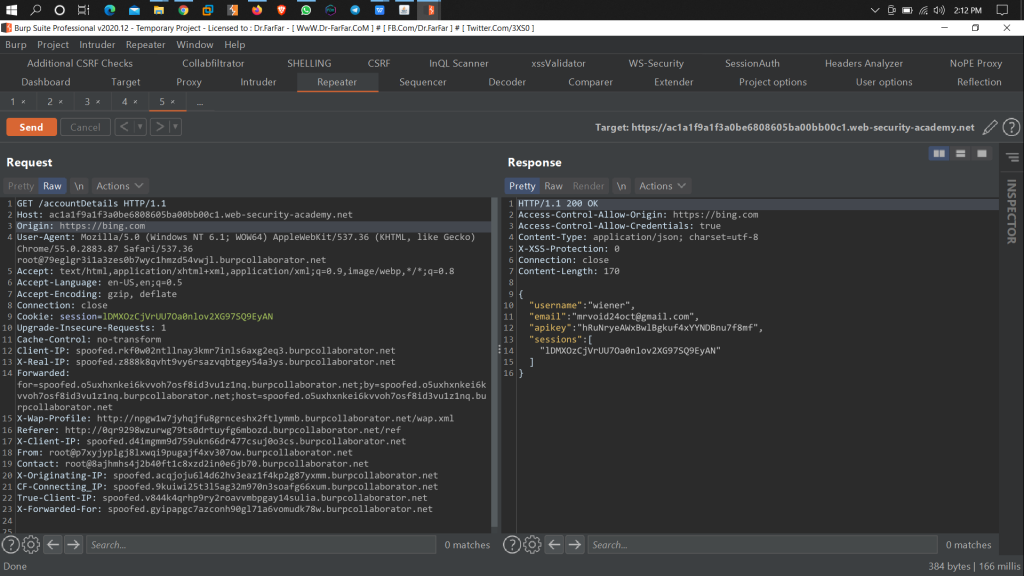
6. If you will get
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: https://bing.com
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: *
7. Then your target site is Vulnerable to CORS
8. If you will get
“Request Block”
Then it secures from CORS
How to prevent CORS-based attacks:-
1. Proper configuration of cross-domain requests
2. Only allow trusted sites
3. Avoid whitelisting null
Author
Chaman



